Concrete flooring is a popular choice in architecture due to its durability, versatility, and modern aesthetic appeal. It is commonly used in both residential and commercial buildings for its ability to withstand heavy loads and high traffic.
Concrete floors can be finished in various ways, such as polished, stained, stamped, or sealed, allowing architects to achieve a wide range of textures and colors.
This type of flooring also contributes to thermal mass, helping regulate indoor temperatures and improving energy efficiency. Additionally, concrete is low-maintenance and long-lasting, making it a sustainable and cost-effective flooring solution in architectural design.
If you want to know about the staircase detail or toilet detail or miscellaneous detail, please click the link.
Image of Concrete flooring detail and downloadable (in DWG) link below
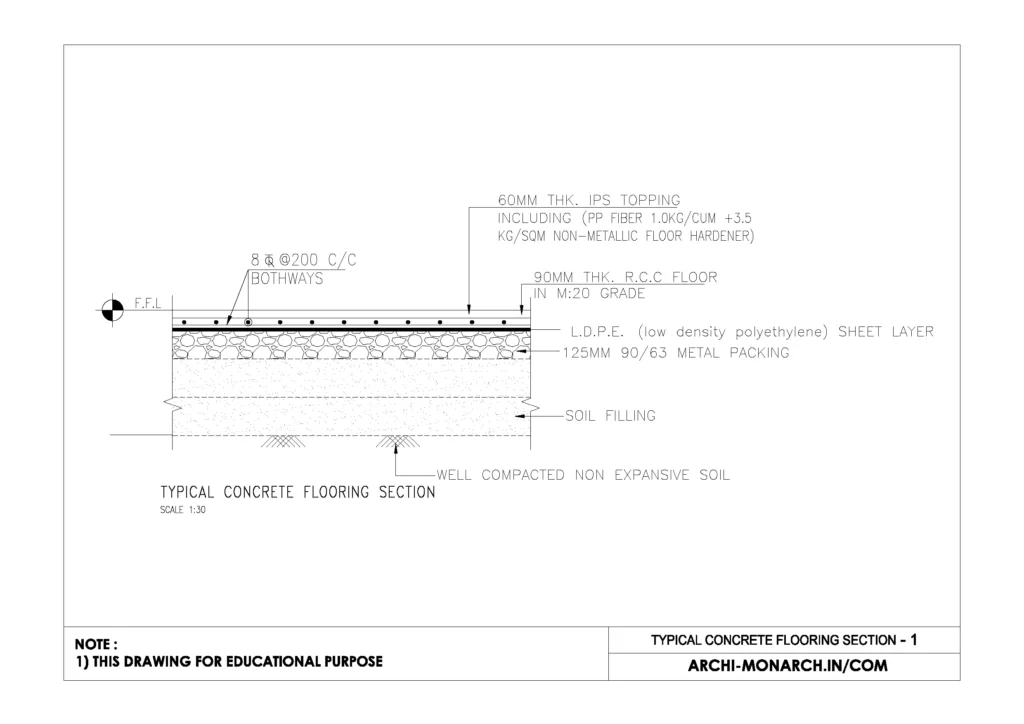
Concrete flooring detail drawing – 1
In construction, a concrete flooring detail drawing provides a technical illustration of how the concrete floor is constructed, showing its layers, dimensions, and connection to other structural elements.
These drawings are essential for builders, engineers, and contractors to ensure proper installation and performance. Here’s an overview of what is typically included:
Concrete Flooring Detail Drawing Components
Subgrade Preparation
- Compacted soil or granular fill
- Geotextile fabric (if needed to prevent soil migration)
Base Layer
- Crushed stone or gravel layer for drainage and leveling
- Thickness usually ranges from 100–150 mm
Vapor Barrier (Optional)
- Polyethylene sheeting to prevent moisture migration from the subgrade into the slab
Reinforcement
- Steel reinforcement mesh (e.g., welded wire mesh) or rebar
- Fiber reinforcement may also be shown
Concrete Slab
- Main structural component, typically 100–150 mm thick for residential and light commercial use
- May include control joints or expansion joints to minimize cracking
Surface Finish
- Troweled, broom-finished, polished, or textured surface depending on usage
- Surface hardeners or sealants might be indicated
Edge and Joint Details
- Dowels for load transfer
- Isolation joints around columns, walls, and other obstructions
Purpose of the Detail Drawing
- Ensures structural integrity and load distribution
- Helps maintain moisture control and thermal performance
- Guides workers during construction for accuracy and quality control
Our tips to help you improve your architectural Concrete flooring detailing.
