Structural glazing is a method of attaching glass to a building structure without the use of mechanical fasteners or adhesives. It is often used in modern architecture to create large, uninterrupted glass surfaces that provide natural light and views while also creating a sense of openness and transparency.
Structural glazing can be used in a variety of architectural applications, including:
- Curtain walls: Curtain walls are exterior walls that are non-structural and typically made of glass and aluminum. Structural glazing is often used to attach the glass panels to the aluminum frame.
- Skylights: Structural glazing is often used to create skylights that allow natural light to enter a building. The skylight is typically made of a glass panel that is attached to the building structure with structural silicone.
- Facades: Structural glazing can be used to create facades that are entirely made of glass. The glass is attached to the building structure with structural silicone.
- Atriums: Atriums are large, open spaces that are typically located within a building. Structural glazing can be used to create walls and roofs for atriums that are made entirely of glass.
Structural glazing provides many benefits such as thermal insulation, energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal. It is a modern design element in architecture and is used in a wide range of building types including commercial, residential and public buildings.
If you want to know about the interior detail or miscellaneous detail or water tank detail, please click the link.
Image of typical structural glazing detail and downloadable (in DWG) link below
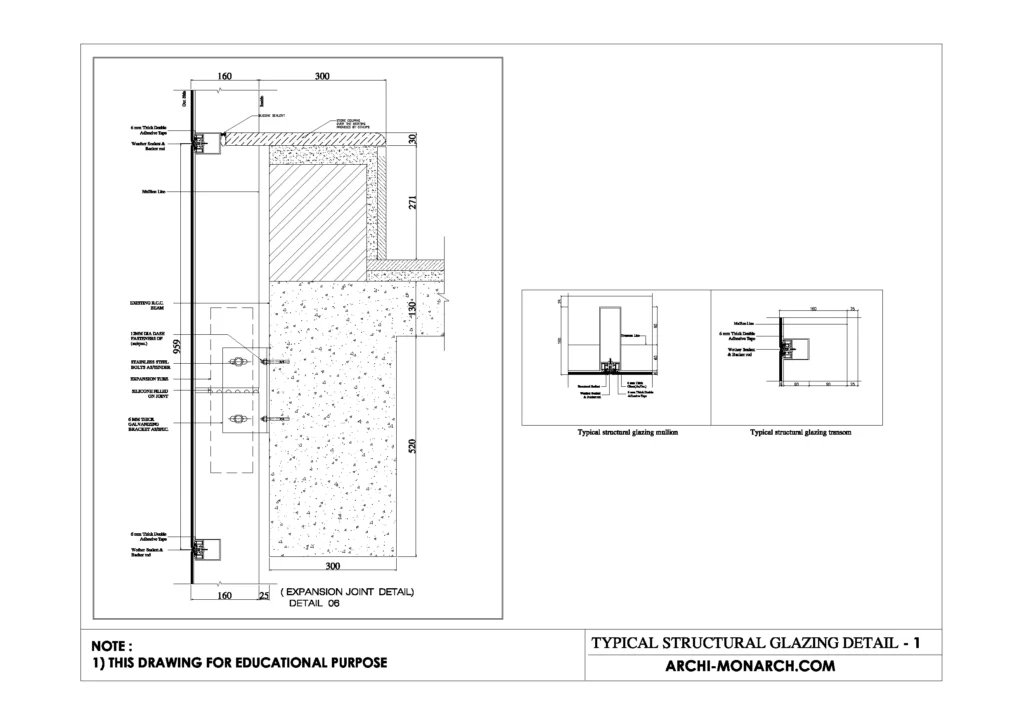
Typical structural glazing detail drawing – 1
A typical structural glazing detail drawing would include the following information:
- A section view of the building showing the location of the structural glazing and how it is connected to the building structure.
- A detailed drawing of the glazing shoe, including dimensions and material specifications.
- A detailed drawing of the glass panel, including dimensions, thickness, and type of glass (tempered, laminated, etc.).
- A detailed drawing of the structural silicone sealant, including the type of sealant and the method of application.
- A detailed drawing of the anchors used to attach the glazing shoe to the building structure, including dimensions and material specifications.
- A note specifying the maximum allowable deflection of the glass panel under load, as well as the maximum allowable joint width between the glass panel and the glazing shoe.
- A note specifying the load-bearing capacity of the glazing system, including wind load, snow load, and seismic load.
- A note specifying the fire-rating of the glazing system.
- A note specifying the water-proofing and air-tightness of the glazing system.
- A note specifying the thermal insulation and solar control properties of the glazing system.
It is important to note that a structural glazing detail drawing should be prepared by a qualified professional, such as an architect or engineer, to ensure that the glazing system meets all building code requirements and the safety standards.
Our tips to help you improve your architectural typical structural glazing detailing.
