
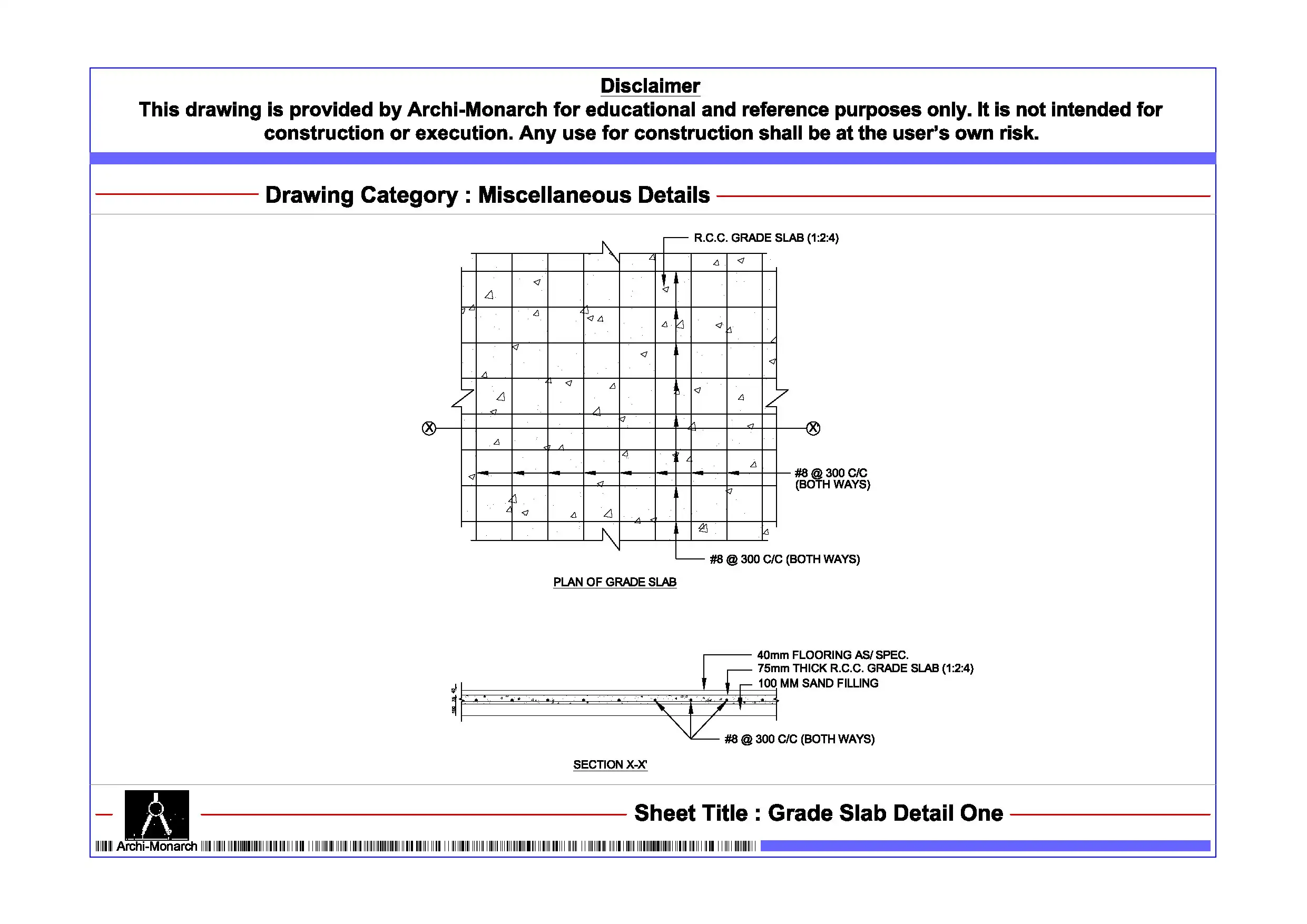
Grade Slab Detail One
Downloadable Architectural Resources for Beginner Architects and Students
Grade Slab Detail One
₹90.0 Original price was: ₹90.0.₹70.0Current price is: ₹70.0.
Hurry up! Flash Sale Ends Soon!
00
DAYS
00
HOURS
00
MINS
00
SECS
Related Drawings
Related products
-
Quick view
Excavation Detail Three
₹100.0Original price was: ₹100.0.₹70.0Current price is: ₹70.0. Add to cartAdd to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
Quick view
Auditorium Section Detail One
₹250.0Original price was: ₹250.0.₹199.0Current price is: ₹199.0. Add to cartAdd to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
Quick view
Auditorium Section Detail Three
₹250.0Original price was: ₹250.0.₹199.0Current price is: ₹199.0. Add to cartAdd to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
Quick view
Classical Order Column Detail One
₹175.0Original price was: ₹175.0.₹149.0Current price is: ₹149.0. Add to cartAdd to WishlistAdd to Wishlist
Recently Viewed Drawings
-
Quick view
Elevation Detail Forty Four
₹175.0Original price was: ₹175.0.₹149.0Current price is: ₹149.0. Add to cartAdd to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
Quick view
Pole Light Foundation Detail One
₹50.0Original price was: ₹50.0.₹40.0Current price is: ₹40.0. Add to cartAdd to WishlistAdd to Wishlist








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.